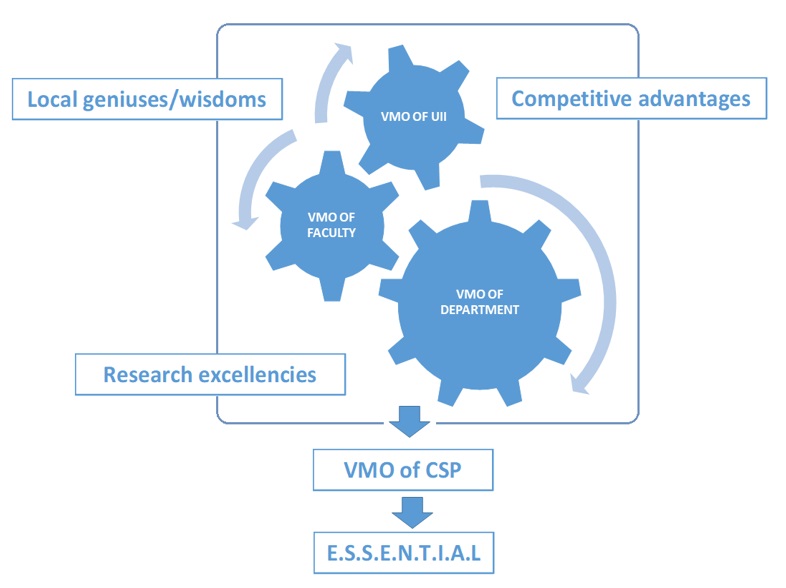
The preparation of the curriculum at the Universitas Islam Indonesia is regulated in rector’s regulation Number 2 / PR / REK / BPA / 2015 concerning Guidelines for Curriculum Preparation. Broadly speaking, the curriculum structure consists of a number of courses to achieve learning in the realm of attitudes, knowledge, general skills, and specific skills. Apart from being based on the Vision, Mission, and Objectives (VMO) of the study program, another aspect that is emphasized in curriculum development is the local genius of the study program. This local genius is a characteristic or differentiator of the CSP with chemistry study programs at other universities. In the preparation of the 2022 curriculum, the Indonesian National Qualifications Framework is used along with several regulations.
In formulating the learning outcomes of graduates, the CSP refers to the Regulation of Minister Research, Technology and Higher Education of Republic Indonesia in 2015 concerning National Standards for Higher Education, the formulation of each graduate of the academic education program, including:
- Attitude Formulation
- Be devoted to God Almighty and be able to show a religious attitude.
- Upholding human values in carrying out duties based on religion, morals, and ethics.
- Contribute to improving the quality of life in society, nation, state, and the progress of civilization based on Pancasila.
- Roles as proud citizens who love the country have nationalism and a sense of responsibility to the state and nation.
- Respect the diversity of cultures, views, religions, and beliefs, as well as the original opinions or findings of others.
- Working together and having social sensitivity and concern for the community and the environment.
- Obey the law and discipline in social and state life.
- Internalize academic values, norms, and ethics.
- Demonstrate an attitude of responsibility for work in their field of expertise independently.
- Internalizing the spirit of independence, struggle, and entrepreneurship.
- General Skill Formulation
- Able to apply logical, critical, systematic, and innovative thinking in the context of developing or implementing science and technology that pays attention to and applies humanities values in accordance with their field of expertise.
- Able to show independent, quality, and measurable performance.
- Able to examine the implications of the development or implementation of science and technology that pays attention to and applies humanities values in accordance with their expertise based on scientific rules, procedures and ethics in order to produce solutions, ideas, designs or art criticisms, compile scientific descriptions of the results of their studies in the form of an undergraduate thesis or final project report, and upload them on the college website.
- Compile a scientific description of the results of the study mentioned above in the form of a thesis or final project report, and upload it on the college page.
- Able to make appropriate decisions in the context of solving problems in their field of expertise, based on the results of information and data analysis.
- Able to maintain and develop networks with mentors, colleagues, colleagues both inside and outside the institution.
- Able to be responsible for the achievement of the results of group work and supervise and evaluate the completion of work assigned to workers under their responsibility.
- Able to carry out the process of self-evaluation of the working group under their responsibility, and able to manage learning independently.
- Able to document, store, secure, and rediscover data to ensure validity and prevent plagiarism.
In addition, in formulating learning outcomes, the CSP uses various references from various sources, including the Indonesian Chemists Association, the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) Accreditation Board, student external studies, and stakeholders consisting of lecturers, students, alumni and stakeholders, where in this case the institution or institution where the user graduates are and the institution that establishes cooperation (Memorandum of Understanding, MoU) in the framework of apprenticeship. Curriculum documents produced by the study program are reviewed by the Academic Development Agency and then ratified by the Rector. The quality of study program curriculum is also evaluated by reputable external parties, in this case the CSP is in the position of international accreditation process from the RSC. Therefore, the preparation of the 2017 Chemistry Curriculum also asked for consideration from the RSC. The characteristics of the curriculum referring to RSC and IPR are assessed from the key requirements of the curriculum which includes several things, namely:
- Depth and breadth of the material: The depth and breadth of the material presented in the lecture. The depth of the material is shown by the syllabus coverage of various basic chemistry competency courses, including courses in physical chemistry, organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and biochemistry. The depth of the material is measured from the learning outcome indicators shown from the example questions that must be mastered by students or students. To achieve this goal, the CSP uses an additional tutorial learning system outside of regular lecture hours. Meanwhile, the breadth of material in the curriculum is shown by various elective courses that are developmental and oriented to industry or technology in the future.
- Graduate skills: Graduates of the CSP must have very adequate laboratory skills to support the appropriate field of work. Input from the RSC was obtained through a remote curriculum consultation (via Skype) with the RSC accreditation body on January 29, 2017. The inputs obtained, among others:
- The increase in the number of Practical Laboratory Work so that the total Practical Laboratory Work hours are at least 300 hours. This is related to the enrichment of graduate skills.
- Added weight for the student’s final project.
- The student’s final semester load is at least 75% of the total activity hours.
- The existence of material enrichment of chemistry competence includes Physical Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, Analytical Chemistry, Organic Chemistry, and Biochemistry. This is achieved through tutorials.
- Elective courses that illustrate the breadth of chemistry topics in various applications along with the development of chemical science internationally.
- Specific Skill Formulation
- Able to carry out general and specific laboratory work as well as synthesis and measurement techniques.
- Able to systematically analyze various alternative solutions in the fields of identification, analysis, isolation, transformation, and synthesis of available chemicals.
- Able to solve problems of Science, Technology and Art in the field of chemistry with the application of relevant technology.
- Able to use software to process and analyze chemical experiment data.
- Able to utilize Big Data, Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI) for problem solving in the field of chemistry.
- Knowledge Formulation
- Mastering theoretical concepts about the structure, nature, function, change, energy and dynamics, identification, separation, characterization, transformation, and synthesis of micromolecular chemicals and their application.
- Mastering operational knowledge of functions, how to operate chemical instruments, as well as data and information analysis of these instruments.
The achievements of graduates from the CSP are prepared by referring to Indonesian National Qualifications Framework, National Standards for higher of Minister of Education and Culture, other laws and adaptations to the MBKM policy and the stages of preparation passed by the CSP which include evaluation of the Graduate Learning Outcomes achievement curriculum, input from stakeholders, formulations from the curriculum development team and discussions involving all lecturers of the UII Chemistry Study Program.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the VMOs and the PLOs
The PLOs are included in the curriculum documents that have been verified by the board of academic development at the Universitas Islam Indonesia (UII) and are evaluated regularly every five years. The statement of the VMOs and the PLOs is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Statement of the VMOs and the PLOs
|
Vision |
Mission |
Symbols |
PLO attributes |
|
Personify Islamic chemists and excel in the application of knowledge in the field of (i) essential oils, (ii) advanced materials for energy and the environment, and (iii) natural products for food and health |
Personalize chemists who have morality (Islamic value: karimah), are innovative, creative, applicative, inspiring, and globally competitive, and are able to synergize education, research, community service, and da’wah Islamiyah reputable nationally and internationally |
E |
Ethics and integrity |
|
S |
Self-esteem and marketing |
||
|
S |
Student of tomorrow |
||
|
E |
Entrepreneurship and employability |
||
|
N |
New and novel idea |
||
|
T |
Teamwork and leadership |
||
|
I |
Information management |
||
|
A |
Adaptability and communication |
||
|
L |
Literacy |
The correlation between profile competence and the PLOs is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Correlation Between Profile Competence and the PLOs
|
No. |
Symbol |
Attribute |
Derivation of the program learning outcomes (PLOs) in learning competencies |
Description of the PLO |
Code |
Aspect of Subject-Specific Criteria (SSC) |
|||
|
Attitude |
Knowledge |
Specific skills |
General skills |
||||||
|
1. |
E |
Ethics and integrity |
√ |
√ |
|
|
Have consistency and enthusiasm in realizing positive and Islamic attitudes and behaviors |
PLO1 |
Social competence |
|
2. |
S |
Self-esteem and marketing |
√ |
√ |
|
√ |
Capable to develop and market themselves sustainably to be able to work and contribute in the area of essential oil development, material for energy and environment, and natural product for food and health |
PLO2 |
Specialist competence |
|
3. |
S |
Student of tomorrow |
|
√ |
√ |
√ |
Endeavor to continue to study (lifelong learning) at a higher level in the relevant field with the chemistry of essential oil development, materials for energy and the environment, and natural products for food and health |
PLO3 |
Specialist competence |
|
4. |
E |
Entrepreneurship and employability |
√ |
|
√ |
√ |
Have the skills to work independently or gain a decent, opportunity-oriented job in the area of essential oil development, materials for energy and the environment, and natural products for food and health |
PLO4 |
Social competence |
|
5. |
N |
New and novel idea |
|
√ |
√ |
|
Have capability and proficiency in critical thinking and problem solving and develop new ideas in the field of essential oil development, materials for energy and the environment, and natural products for food and health |
PLO5 |
Specialist competence |
|
6. |
T |
Teamwork and leadership |
√ |
|
|
√ |
Have leadership skills and productive attitudes toward cooperating (collaborating) or interacting with others in many levels of challenge |
PLO6 |
Social competence |
|
7. |
I |
Information management |
|
√ |
√ |
√ |
Have the ability to collect, analyze, and organize information from various sources using the latest information technology in chemistry journals and databases related to essential oil development, materials for energy and the environment, and natural products for food and health |
PLO7 |
Specialist competence |
|
8. |
A |
Adaptability and communication |
√ |
|
|
√ |
Have capability and proficiency in the association of the chemistry global community and social awareness that supports chemistry science |
PLO8 |
Specialist competence |
|
9. |
L |
Literacy |
|
√ |
√ |
√ |
Have scientific, digital, and computer proficiency, internet literacy, and mastery of international language skills to support research and development in chemistry. |
PLO9 |
Specialist competence |