The bachelor’s chemistry degree curriculum is designed to be completed within four academic years (eight semesters) and consists of 144 semester credit units (SCUs):134 for compulsory courses and 10 for elected courses. As can be seen in Figure 1, after the SCU unit is converted into ECTS, it is consisting of 244.8 ECTS, which is consist of 227.8 ECTS for compulsory courses and 17 ECTS for elected courses. The compulsory courses consist of general university courses (30.6 ECTS) and chemistry courses (197.2 ECTS) including organic, inorganic, physical, and analytical chemistry, as well as biochemistry. The elective courses are divided into three areas, including chemical entrepreneurship, chemical industry, and energy & environment.
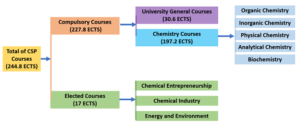
Figure 1. The Chemistry Courses in ECTS
The academic workload per semester in CSP curriculum is presented in Table 2. Course modules are completed in eight semesters (four years), with the total workload of 6612.32 hours. The student workload is one credit for a theoretical course, which is equal to 50 minutes of in-class learning, 60 minutes of independent study, and 60 minutes of weekly assignments (16 weeks per semester). Meanwhile, one credit for a practical course is equal to 170 minutes of practical work per week which is consist of worksheets and pretest preparations, laboratory work, group discussion, literature searching, and report writing (16 weeks per semester). The comparison for workload of theory and laboratory work is presented in Table 3.
Table 2. Academic Workload per Semester in CSP Curriculum
| Compulsory Courses | Credit | ECTS | Workload (hours) | ||||||
| Semester | Total | Semester | Total | Semester | Total | ||||
| I | II | I | II | I | II | ||||
| 1st Year | 20 | 20 | 40 | 34 | 34 | 68 | 952 | 952 | 1904 |
| 2nd Year | 19 | 20 | 39 | 32.3 | 34 | 66.3 | 904.4 | 952 | 1856.4 |
| 3rd Year | 21 | 20 | 41 | 35.7 | 34 | 69.7 | 999.6 | 952 | 1951.6 |
| 4th Year | 8 | 6 | 14 | 13.6 | 10.2 | 23.8 | 138.72 | 285.6 | 424.32 |
| Total Compulsory Courses | 134 | 227.8 | 6136.32 | ||||||
| Total Elected Courses | 10 | 17 | 476 | ||||||
| Grand Total | 144 | 244.8 | 6612.32 | ||||||
Table 3. Workload Comparison of Theory and Laboratory Work
| Courses | Credit | ECTS | Duration in Hours | Percentage (%) |
| Theory* | 130 | 221 | 2946.67* | 73.20 |
| Laboratory Work** | 14 | 23.8 | 1078.93** | 26.80 |
| Total | 144 | 244.8 | 100% | |
| Calculation of Duration in hours: | ||||
| * (221x16x50)/60 | ||||
| ** (23.8x16x170)/60 |
Skills are integrated into regular coursework and are taught by the subject lecturer. The teaching of skills is also facilitated by specific types of assignments. These assignments provide students with work experience with emerging tools (and already emerged tools), such as wikis, Google Scholar, and online scientific literature tools. Each of these assignments asks students to engage in work typical of standard chemistry education—e.g., reading, writing, and discussion—with the goal of instilling in students an effective understanding of and applied expertise in current scientific developments. While they are polishing these skills, the students are also learning to use new and different tools. During tutorial sessions, students are encouraged to present work and develop problem solutions, for which they receive constructive feedback. As part of their final year report, students receive targeted guidance on report writing.
For the professional skill in chemistry, some practical works are designed in the practical courses. The mapping of laboratory skill is matched with their level and theories gained in the class. The evaluation of laboratory skill covers safety skill, attitude and technical skill, and report and analysis skill.




